Editor’s Note: Today’s post is by Mandy Brannon, Kate Heaney, Jacklyn Lord, and Cason Lynley. Mandy is the Journals and Collections Marketing Manager at Duke University Press. Kate is a Lead Product Manager at Clarivate. Jacklyn is the Marketing and Operations Manager for the Society for Scholarly Publishing. Cason is the Director of Marketing, Sales, and Finance for books and journals at Duke University Press.
In Memoriam: This project was partially conceived by Sarah Andrus, who passed away in October 2022. Sarah was Executive Publisher at Mary Ann Liebert since 2021 and previously worked at Oxford University Press and Wiley. She co-authored the book Leading from the Middle, a resource that shares empowering messages to help readers take control of their environment by seeing themselves as actionable leaders today. She worried greatly about the decline of science in popular discourse, and her diligent work to support research will be her legacy. A member of SSP since 2019, Sarah was an active volunteer for the Career Development Committee and the Joint Task Force for Career Progression. She was integral to developing SSP’s Publishing Skills Map and the Career Progression project.
The Society for Scholarly Publishing (SSP) Career Development Committee is pleased to announce the 4th annual Professional Skills Survey and updated Professional Skills Map. Many thanks to all who participated!
The 2023 survey received 235 responses and asked publishing professionals at all career levels across the industry to indicate which personal characteristics, transferable/interpersonal skills, and technical/knowledge-based skills are essential to success in their respective positions. Respondents also identified skills they would most like to develop further, highlighting opportunities for training and mentorship in those areas as they advance in their careers.
For this survey iteration, some questions and options were updated to match the information and data collected by the AUPresses/SSP/ALSPS Career Progression Taskforce while balancing the need to compare the 2023 data to past Skills Survey data. To do this, we carefully reviewed each project’s questions and identified those that overlapped by asking about the same skill set. For example, the semi-opened variable, “Current Role,” was replaced with two separate variables, “Functional Area” and “Product Role,” making comparisons across similar roles in books and journals more direct.
By mapping identified skill sets to associated roles, we aim to help publishing professionals recognize their core strengths and areas for further development while encouraging exploration of new or overlooked roles that align with their interests and competencies. The Professional Skills Map is a powerful tool for exploring individually or with a mentor to identify necessary skills for a current or desired role.
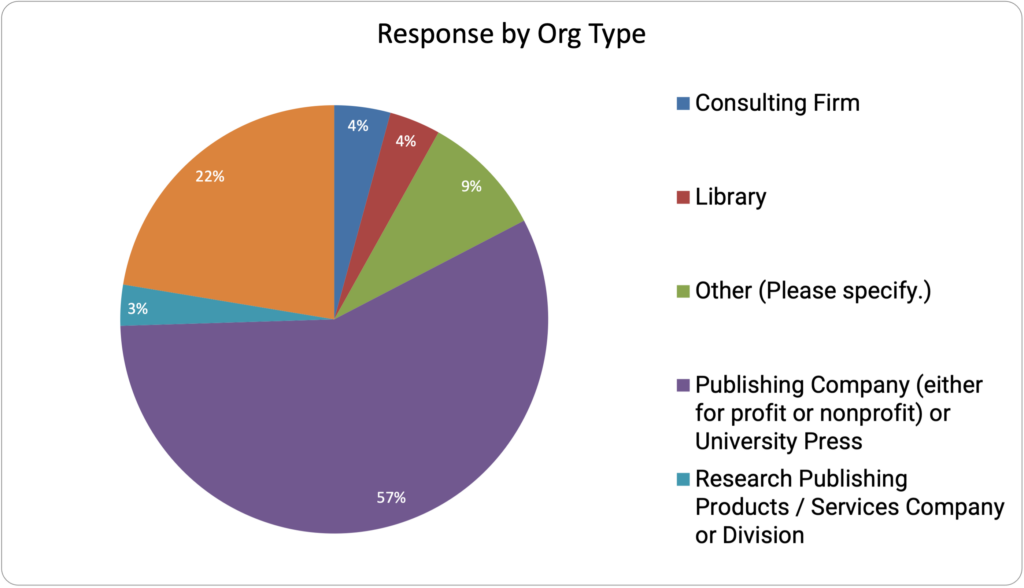
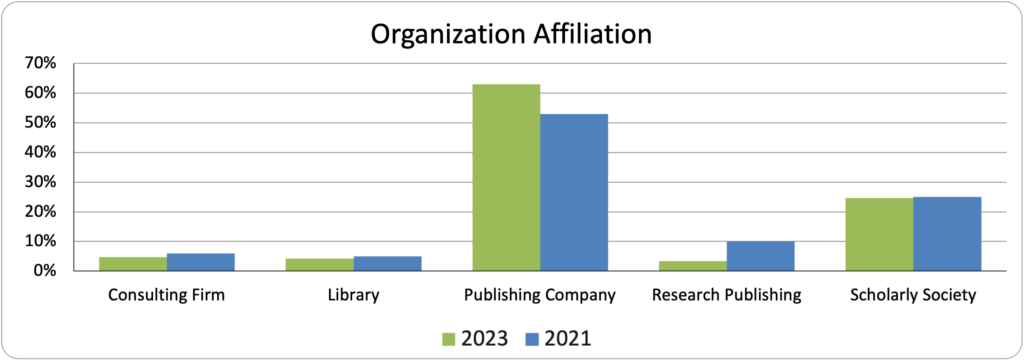
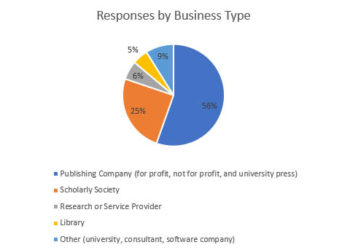
Among the respondents,148 were from Publishing Companies, 58 were from Scholarly Societies,10 were from Libraries, 11 were involved in Consulting, and 8 were Research or Service Providers. This breakdown varies from 2021, as fewer Research Service Providers responded to the survey. Unsurprisingly, over 60% of the respondents are affiliated with Publishing Companies, either private, public, or nonprofit. The percentage of respondents from Libraries and Scholarly Societies remained relatively flat over the survey interval.
The graphs presented here show breakdowns of the most common answers across all survey respondents
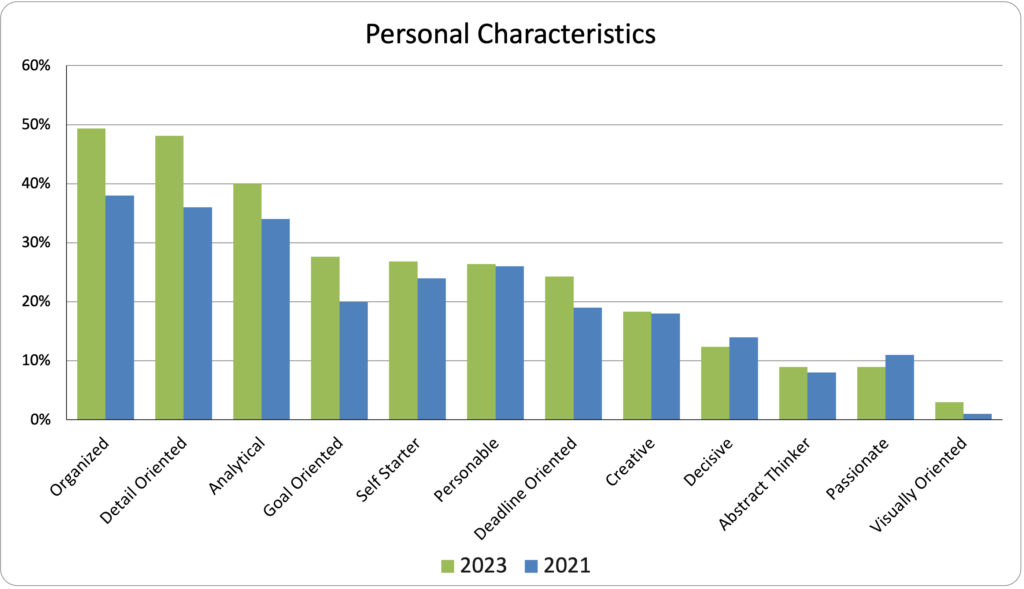
Most Common Personal Characteristics Across Respondents
Top 5 Personal Characteristics for 2023
| Organized | 49% |
| Detail Oriented | 48% |
| Analytical | 40% |
| Goal Oriented | 28% |
| Self Starter | 27% |
Comparing 2023 to 2021, Detail-Oriented and Organized remain the top Personal Characteristics across all roles. In 2021, Strategic was included as a Personal Characteristic and was a top three skill but removed from the list in the 2023 survey due to being addressed in other questions. It’s possible that Analytical moved into the third most reported Personal Characteristics increased due to the elimination.
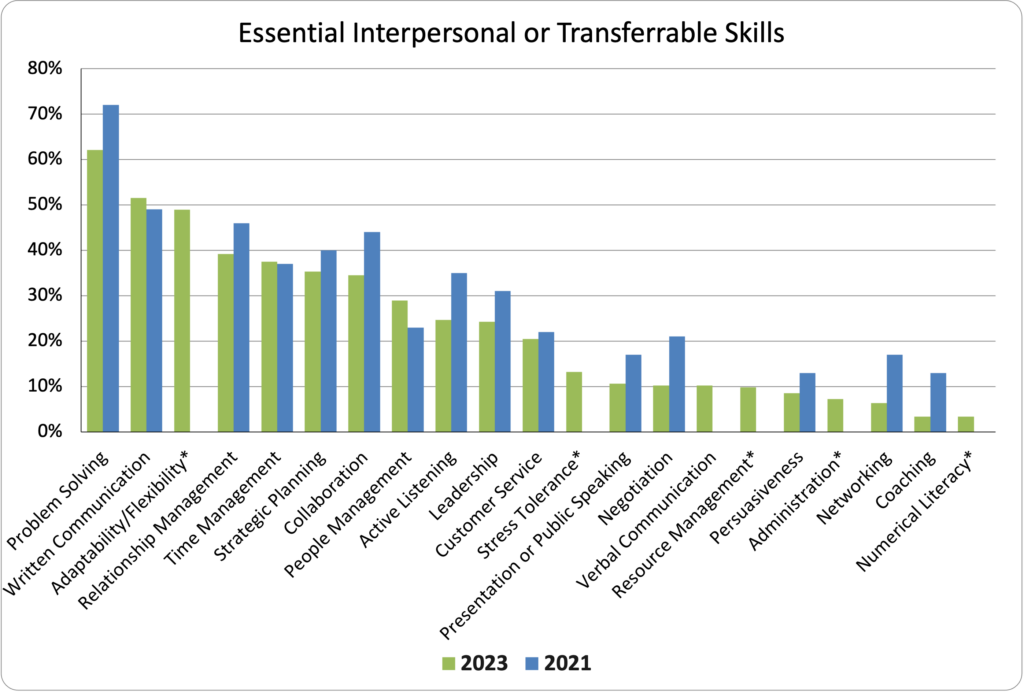
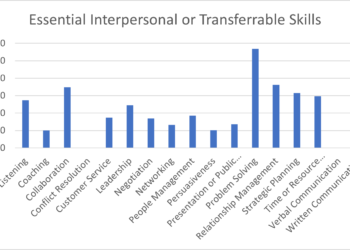
Most Common Essential Interpersonal or Transferable Skills Across Respondents
Top 5 Essential Interpersonal Skills for 2023
| Problem-Solving | 62% |
| Written Communication | 51% |
| Adaptability/Flexibility* | 49% |
| Relationship Management | 39% |
| Time Management | 37% |
Since 2021, Adaptability/Flexibility has been a new addition to Essential Interpersonal or Transferable Skills. Given that it is the third highest-rated skill, its importance is evident, especially in light of the pace of change in the industry. Based on our work with the Career Progression Taskforce, several Interpersonal and Transferable Skills were added to the survey, including stress tolerance, resource management, numerical literacy, administration, verbal communication, and adaptability/flexibility.
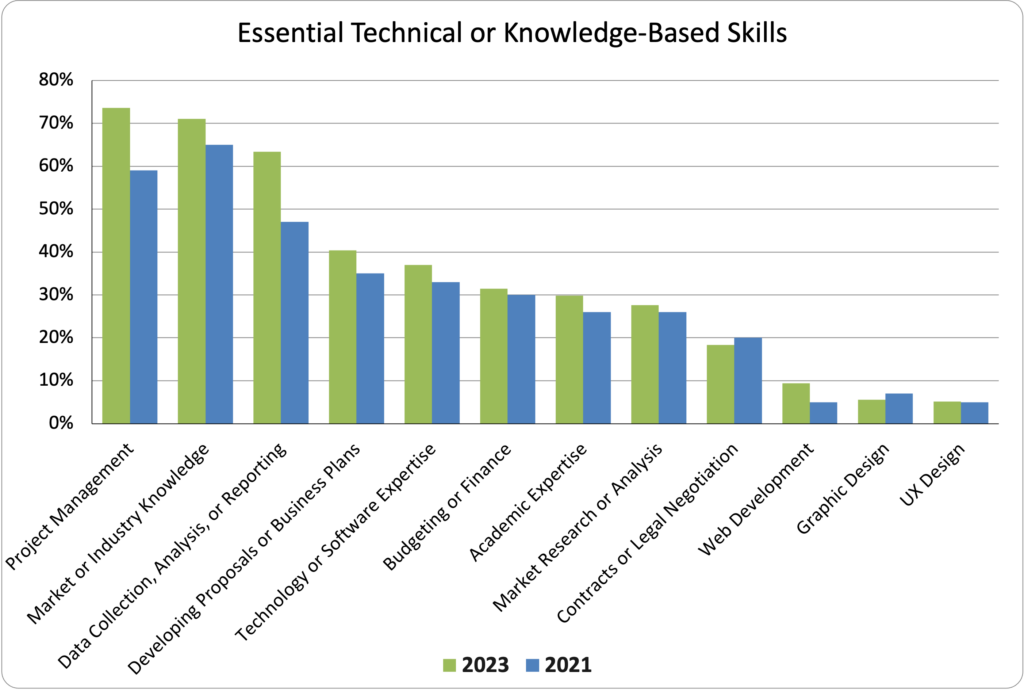
Most Common Essential Technical or Knowledge-Based Skills Across Respondents
Top 5 Essential Technical or Knowledge-Based Skills for 2023
| Project Management | 74% |
| Market or Industry Knowledge | 71% |
| Data Collection, Analysis, or Reporting | 63% |
| Developing Proposals or Business Plans | 40% |
| Technology or Software Expertise | 37% |
Project Management became the top Essential Technical or Knowledge-Based Skill, slightly ahead of Market or Industry Knowledge. The two skills switched places between 2021 and 2023, which may indicate a notable shift in job responsibilities. Data Collection, Analysis, or Reporting also saw significant growth.
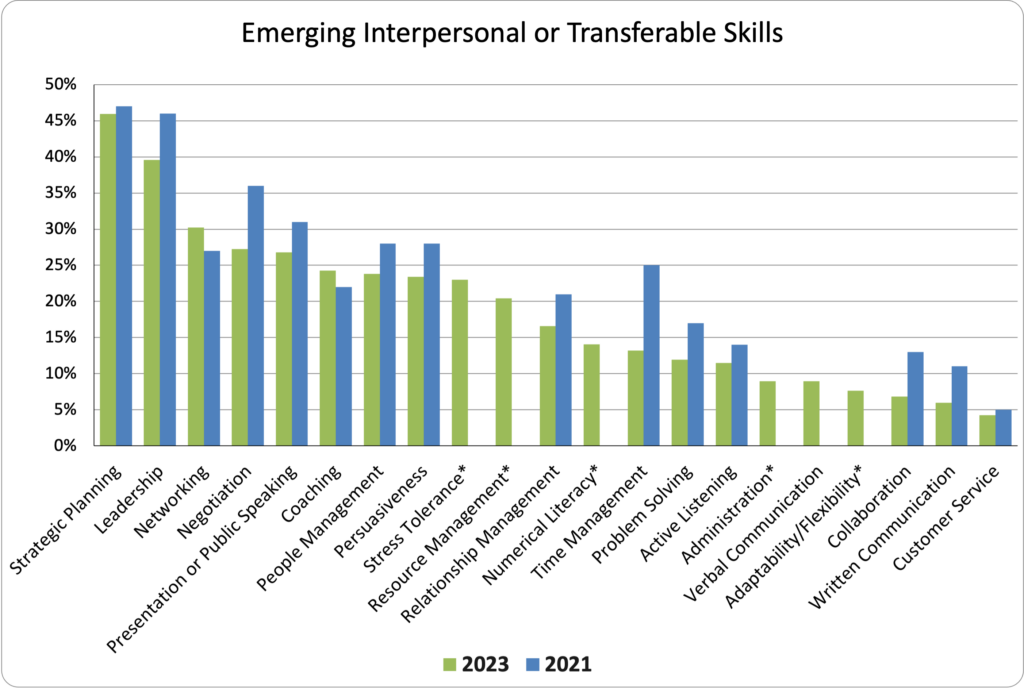
Most Common Emerging Interpersonal or Transferable Skills Across Respondents
Top 5 Emerging Interpersonal Skills for 2023
| Strategic Planning | 46% |
| Leadership | 40% |
| Networking | 30% |
| Negotiation AND Presentation or Public Speaking | 27% |
| Coaching AND People Management | 24% |
Strategic Planning and Leadership remained the top Emerging Interpersonal or Transferable Skills. Negotiation and Presentation or Public Speaking tied for fourth place, while Coaching and People Management tied for fifth. New skill Stress Tolerance was rated most highly at 23% as an emerging area.
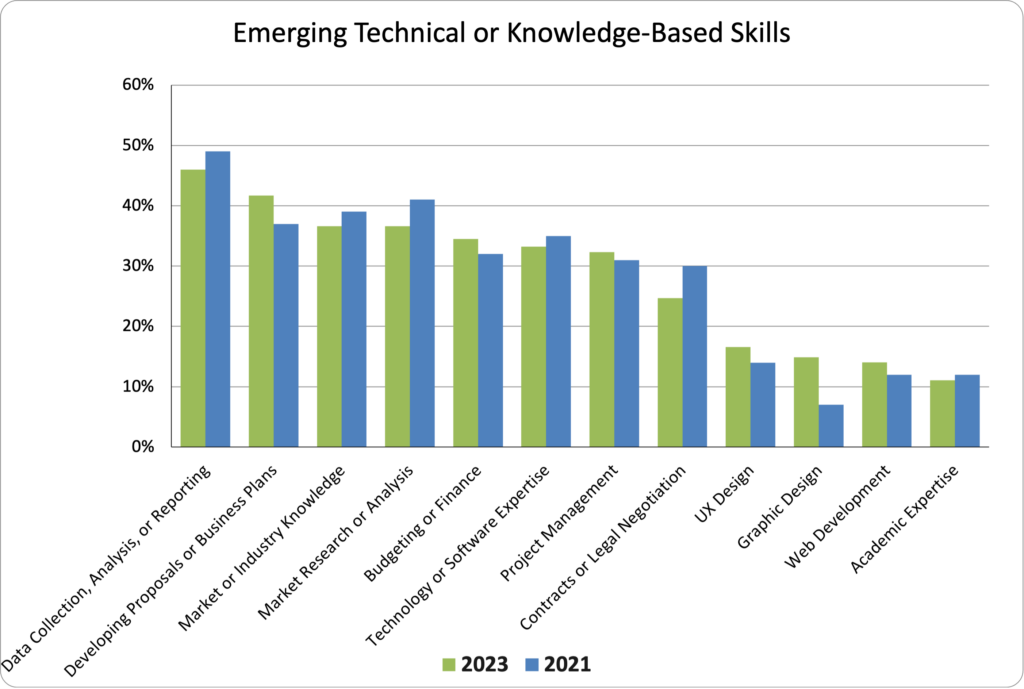
Most Common Emerging Technical or Knowledge-Based Skills Across Respondents
Top 5 Emerging Technical or Knowledge-Based Skills for 2023
| Data Collection, Analysis, or Reporting | 46% |
| Developing Proposals or Business Plans | 42% |
| Market or Industry Knowledge | 37% |
| Market Research or Analysis | 37% |
| Budgeting or Finance | 34% |
| Technology or Software Expertise | 33% |
Data Collection remains the top reported emerging Interpersonal or Transferable Skill, which is unsurprising given the interest in open data and reproducibility concerns. Market Research or Analysis, Market or Industry Knowledge, and Developing Proposals or Business Plans all moved around but remain in the top five reported Emerging Technical or Knowledge-Based Skills.
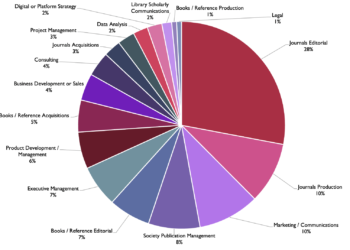
Top Responses by Functional Area
| Which of the following best describes the functional area of your current role? | |
| Accounting | 1% |
| Acquisitions | 6% |
| Administration | 6% |
| Design and Production | 6% |
| IT | 4% |
| Manuscript Editorial | 28% |
| Marketing | 11% |
| Operations | 17% |
| Rights and Permissions | 0% |
| Sales | 6% |
Among Editorial roles at Publishing companies, the most commonly reported group, respondents characterized themselves as detail-oriented and organized, with analytical skills and a focus on deadlines. Operations across the board are similarly strong in analytical thinking, detail-oriented, organized, personable, and self-starters. Marketing and Communications reported the importance of organizational skills, creativity, and being goal-oriented and personable. While tied in the number of responses, Administrative and Acquisition roles varied. Administrative highlighting detail-orientation and organization (similar to Editorial and Operations) and Acquisitions identified being personable, a self-starter, and goal-oriented as essential traits. For Sales, analytical thinking held the top position, followed by a three-way tie for being personable, goal-oriented, and organized.
Across the functional roles, publishing professionals are primarily hoping to develop their skills in data collection and analysis, business plan development, and market research or knowledge. There has been an increase in reported interest in project management and budgeting over previous years.
To see further how the characteristics and skills apply to particular publishing roles, visit the Skills Map.
Top Responses by Decision-Making Authority
| What is the level of decision-making authority in your current role? Consider how critical it would be if you made a mistake that was not readily correctable. | |
| Top position in the organization. CEO, President, Publisher, Press Director | 5% |
| Top position in the department | 21% |
| Authority to make departmental or program decisions autonomously and in the absence of the department head | 14% |
| Departmental or program decisions subject to higher approval before implementation | 28% |
| Limited decision-making, e.g., product level | 27% |
| No decision-making authority | 4% |
Several data points of particular interest were the similarities and differences in the characteristics valued by respondents with varying levels of decision-making authority. Respondents who claimed “No decision-making power” and “limited decision-making” value “detail-oriented” and “organized” as the characteristics that are most essential to their success. Those respondents with departmental or program decision-making, or those whose program and departmental decisions are subject to approval, continue to value “detail-oriented” and “organized” as well as “analytical” as their most essential qualities. However, respondents who are decision-makers in top positions of departments or organizations value “creative,” “abstract thinking,” and “goal-oriented” as those characteristics essential to their success. “Project management” and “industry knowledge” were highly valued as technical or knowledge-based skills essential to success across all levels of decision-makers. When asked about interpersonal or transferable skills that one would most like to develop for future career goals, networking, coaching, leadership, and strategic planning are top responses for all levels of decision-makers.
The interactive Professional Skills Map is divided into six organization types at the top level, followed by the functional areas reported by survey respondents (you can find the percentage of respondents listed after each role). Each role can be expanded to reveal the desirable personal characteristics, essentials for success, and emerging needs for that role. Skills and characteristics at the end of each branch indicate the percentage of respondents who endorsed that item.
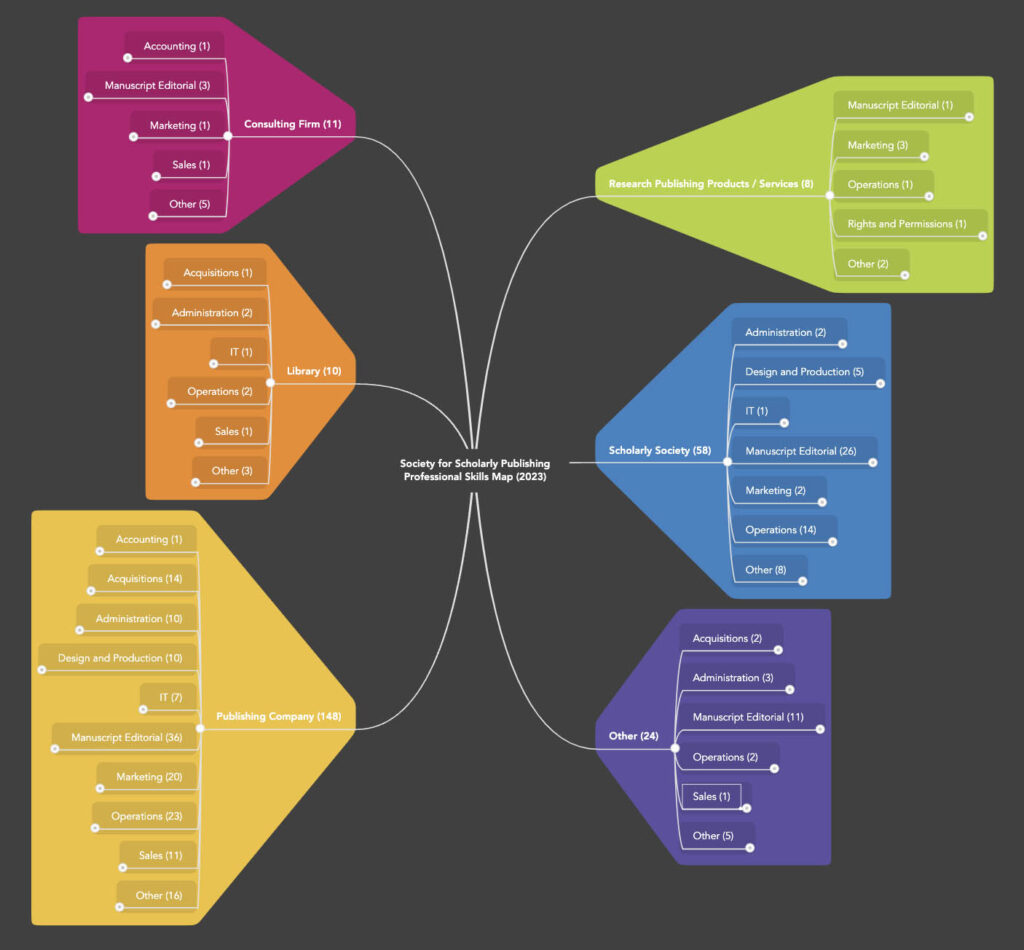
Look at the updated map and let us know how it has helped you identify skills to develop or caused you to think differently about your career path. We also welcome any other feedback to help improve the survey or map.